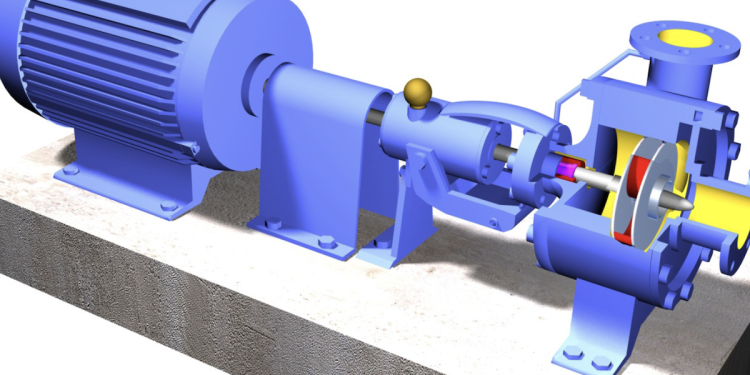
A pump is a mechanical device that moves fluids or gases from one place to another. An electric motor or a combustion engine is usually used to power a pump. A pump uses a motor to drive an impeller or rotor, which creates a vacuum that pulls liquid into the pump body. The impeller then forces the liquid out of the pump, creating pressure that moves the liquid through a pipe or other housing.
One of the most common types of pumps is the centrifugal pump. The basic design of a centrifugal pump is simple. The impeller is a disc-shaped blade that is attached to a rotating shaft. The rotating impeller creates a centrifugal force, which pushes the fluid out of the pump. The impeller is usually enclosed in a housing containing the vanes or blades that direct the fluid.
Centrifugal pumps are classified as either single-stage pumps or multi-stage pumps. Single-stage pumps are used for low-pressure applications, such as water systems, while multi-stage pumps are used for higher-pressure applications, such as industrial processes.
Centrifugal pumps are efficient, reliable, and require low maintenance. However, they are unsuitable for all applications and are prone to cavitation and vibration. Centrifugal pumps are used in many applications, including water systems, industrial processes, and marine applications.
Pumps are essential machinery in a variety of industries and settings. Pumps help to move liquids, gases, and other materials from one location to another. As one of the most versatile machinery, pumps are helpful for many applications.
In commercial environments, pumps are used in a variety of ways. They are used to pump water from wells, maintain water pressure in homes, circulate water in pools, and provide water from rivers and lakes. They are also used to move chemicals, such as those used in swimming pools, and to provide air for ventilation purposes.
In the industrial world, pumps are used to move oil, gas, and other materials in oil and gas production, chemicals in manufacturing, and wastewater in wastewater treatment plants. Pumps are also essential in medical settings. They are used to pump blood and move fluids in dialysis machines. They also move air in respirators and inflate balloons during medical procedures.
Factors to consider when choosing a pump
- Flow Rate: Consider the desired flow rate of the pump. Different pumps have different flow rates, so it is vital to determine which type of pump can meet the application’s needs.
- Efficiency: Look for an efficient pump designed to use less energy. Energy-efficient pumps can reduce operational costs.
- Size: Consider the size of the pump. You must ensure the pump can fit in your space and have the necessary power to operate correctly.
- Pressure affects the pump directly. If the pressure is too high for the pump to withstand, it can cause internal leakage and damage to pump parts.